- Article
Macro-Financial Blind Spots in Emerging Markets: Non-Bank Intermediation, Funding Liquidity, and the Persistence of Global Shock Transmission
- Gustavo Henrique Rodrigues Pessoa and
- Ricardo Ratner Rochman
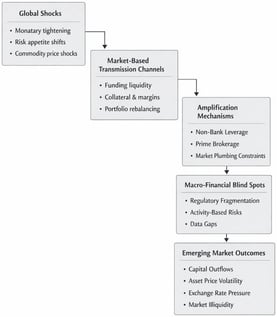
Despite significant advances in bank regulation and the widespread adoption of macroprudential frameworks, emerging market economies remain persistently vulnerable to global financial shocks. Episodes such as the Global Financial Crisis, the COVID-19 market turmoil, and recent monetary tightening cycles reveal that financial stress originating in core markets continues to transmit rapidly and forcefully to emerging economies. This paper argues that such vulnerability reflects structural features of contemporary financial systems rather than deficiencies in domestic banking regulation alone. Adopting a conceptual and analytical approach, the article develops an integrated framework of macro-financial blind spots that links global financial cycles, non-bank financial intermediation, and regulatory fragmentation. The analysis highlights how funding liquidity, collateral valuation, margin dynamics, and market-based leverage amplify global shocks through channels that lie largely outside traditional, bank-centric macroprudential frameworks. As market-based finance expands, systemic risk increasingly originates in activities rather than institutions, limiting the effectiveness of entity-based regulation and reinforcing emerging markets’ role as price-takers in global portfolios. The paper contributes to the literature by synthesizing insights from macroprudential policy, market liquidity, and non-bank finance to explain the persistence of emerging market vulnerability in an era of globalized funding. It further derives policy implications for macro-financial governance, emphasizing the need for system-wide, activity-based approaches, improved data and transparency, and stronger domestic and international regulatory coordination. These findings are relevant for policymakers seeking to reconcile financial integration with systemic resilience in emerging markets.
5 February 2026